Introduction
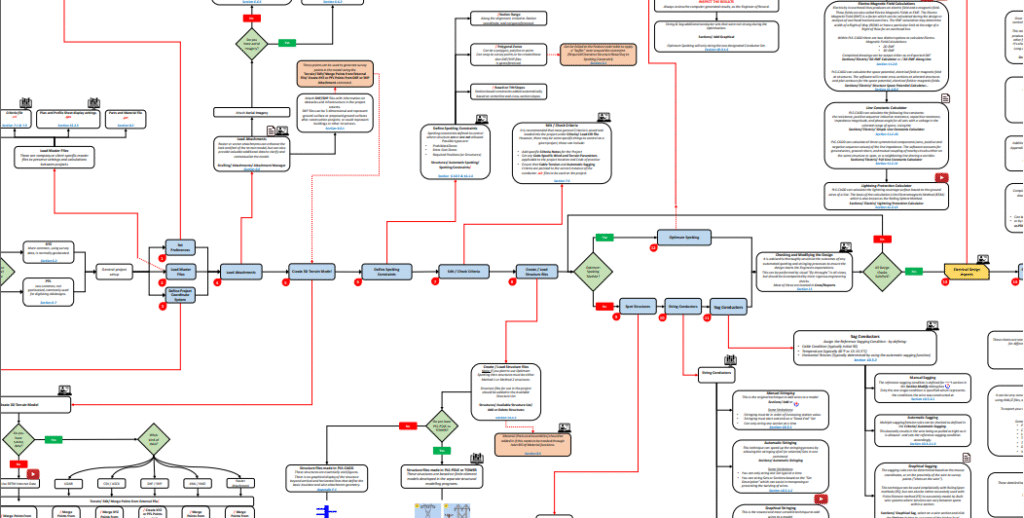
Designing and analyzing overhead transmission lines requires a powerful and systematic approach. PLS-CADD (Power Line Systems – Computer Aided Design and Drafting) is one of the most widely used software solutions in the industry. It provides a structured workflow that covers everything from terrain modeling to construction reports.
This article explains the step-by-step PLS-CADD workflow, highlighting its unique features and how it helps engineers design cost-effective, safe, and optimized transmission lines.
Step 1: Setting Up the Project
The first step is to create a project directory and choose the project type. PLS-CADD supports:
- XYZ Projects – Based on geolocated survey data (most common).
- PFL Projects – Non-geolocated, often used for digitizing old designs.
You can also load master files (.fea, .cri, .prt, .pps) to ensure consistency in standards across multiple projects.
Step 2: Terrain and Survey Data Integration
PLS-CADD allows engineers to integrate survey data from multiple sources, including:
- LiDAR data (LAS/LAZ files)
- CSV/ASCII survey points
- DXF/SHP attachments for obstacles
- Aerial imagery via WMS (Web Mapping Service)
Once data is imported, a 3D terrain model is created, enabling precise alignment and clearance checks.
Step 3: Defining Constraints and Criteria
Engineers can define:
- Spotting Constraints – Prohibited zones, required positions, or extra cost areas.
- Criteria Files – To enforce wind, terrain, sagging, and conductor tension requirements.
This ensures that all designs comply with project codes and safety regulations.
Step 4: Structure Spotting and Placement
Structures can be manually or automatically spotted:
- Manual Spotting – Placing structures along alignments or freehand.
- Automatic Spotting – Using algorithms to place angle or suspension structures efficiently.
- Optimum Spotting Module (Unique Feature) – A paid add-on that uses advanced optimization algorithms to minimize costs and improve efficiency.
Step 5: Stringing and Sagging Conductors
PLS-CADD offers multiple methods for conductor installation:
- Automatic Stringing – Fast, but limited to one set type at a time.
- Graphical Stringing – Versatile, allowing wire transposition, skipped structures, and XY-based modeling.
- Manual Stringing – Traditional method requiring sequential station input.
- Sagging Methods – Automatic, graphical, or manual sagging to define conductor conditions and ensure safe clearances.
Step 6: Electrical Design Aspects
Another unique strength of PLS-CADD is its integrated electrical design tools, including:
- Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Calculations – 2D and 3D field analysis.
- Thermal Rating – Based on IEEE, CIGRE, or TNSP standards.
- Line Constants Calculator – For impedance and symmetrical component calculations.
- Lightning Protection – Using Electromagnetic/Rolling Sphere Method.
- Circuit and Phase Labeling – For plan & profile drawings and phasing diagrams.
ALSO READ: PLS-CADD Software Interface: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Step 7: Plan & Profile Sheets and Reports
Once the design is verified, PLS-CADD can generate:
- Plan & Profile Sheets – With customizable layouts, annotations, and DXF attachments.
- Construction Reports – Stringing charts, staking reports, structure load reports, and bills of materials.
- KMZ Exports – To share models and reports in Google Earth for easy visualization.
What Makes PLS-CADD Workflow Unique?
Unlike many CAD tools, PLS-CADD integrates survey data, structural analysis, electrical calculations, and drafting into one platform. Some standout features include:
- Optimum Spotting Module – Reduces costs by optimizing structure placement.
- Integrated EMF & Lightning Calculations – Rare in most line design software.
- Dynamic Reporting – Auto-updates all drawings and reports when the model changes.
- 3D Terrain Modeling with LiDAR Integration – Ensures real-world accuracy.
Conclusion
The PLS-CADD workflow provides a comprehensive solution for power transmission line design. From survey data to construction reports, it ensures engineering accuracy, regulatory compliance, and cost optimization.
Whether you are a beginner learning the basics or an experienced engineer handling complex projects, PLS-CADD’s structured workflow makes the process efficient and reliable.
DOWNLOAD :

Pingback: Understanding Transmission Line Unbalance and Transposition: A Simple Guide - ohtldesign.com