What is Right-of-Way (ROW)?
In transmission line engineering, the Right-of-Way (ROW) is a strip of land acquired to construct, operate, and maintain overhead power lines. The transmission line is usually centered within this corridor, and the ROW ensures safety, reliability, and accessibility of the system.
ROW width depends on:
- Voltage level of the line
- Type of support structures (lattice tower, monopole, wood pole, etc.)
- Conductor sag and swing under wind pressure
- Clearances to ground, buildings, and roads
Input Data Required for Right-of-Way (ROW) Calculation
To calculate the Right-of-Way (ROW) for an overhead transmission line, certain technical parameters must be defined in advance. These inputs ensure that the calculation covers electrical, mechanical, and structural aspects of the line.
The required data items are as follows:
- Maximum Line Voltage
- Type of Structure
- Drawing for Tower Type
- Distance, tower center to V-String center
- Number of Insulators in V-String
- Insulator String Length (including hardware)
- Conductor Type
- Stranding
- Weight per Unit Length
- Diameter of Conductor
- Ruling Span
- Sag at specified temperature and wind pressure
👉 These twelve parameters form the basis for ROW width calculation, allowing engineers to apply clearance formulas and determine the safe corridor required for the transmission line.
Example: ROW Width Calculation for a 380 kV Double Circuit Line
Q. Make a ROW calculations for a 380kV double circuit steel tower with V-Suspension insulator string (46 X 2 units of aero form type cap & pin disc insulators), and ACSR/AW Condor conductor with 400 meters ruling span.
Information needed to determine the right-of-way requirements for structure types of any transmission lines are tabulated below:
Table : Sample Data for Right-of-Way (ROW) Calculation
| Sr. No. | Description | Circuit No. 1 & 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maximum Line Voltage | 380 kV |
| 2 | Type of Structure | Lattice Steel (vertical configuration) |
| 3 | Drawing for Tower Type | S1N XYZ |
| 4 | Distance, tower center to V-String center | 7.60 m |
| 5 | Number of Insulators in V-String | 46 × 2 |
| 6 | Insulator String length (including hardware) | 7.5 m |
| 7 | Conductor Type | ACSR/AW Condor |
| 8 | Stranding | 54/7 |
| 9 | Weight per Unit Length | 1.461 kg/m |
| 10 | Conductor Diameter | 27.72 mm |
| 11 | Ruling Span | 400 m |
| 12 | Sag at 25°C with 927 N/m² wind | 13.0 m (approximate) |
SOLUTION:
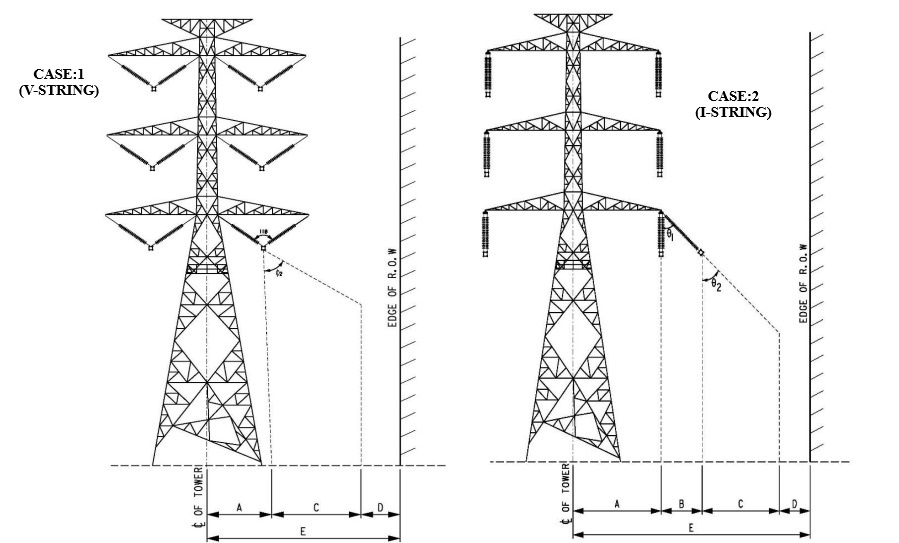
ROW Calculation for 380 kV Double Circuit Tower with V-String Insulators
This calculation determines the required Right-of-Way (ROW) width for a 380 kV transmission line using a lattice steel vertical tower (Tower Type S1N), with V-suspension insulator strings.
It is based on:
- The drawing showing both V-string (left tower) and I-string (right tower) configurations.
- The table labeled above provides key design data.
⚙️ Structure Overview
- Voltage Level: 380 kV
- Tower Type: Lattice Steel (Vertical Configuration)
- Tower Drawing Reference: XYZ
- Conductor: ACSR/AW Condor
- Configuration Used in Calculation: V-String (left-side tower in the drawing)
Step-by-Step Calculation
Step (a): Dimension A – Tower Center to V-String Center
From tower drawing:
A = 7.60 m
Step (b): Dimension B – Offset Due to Insulator Deflection
For V-string configuration, deflection angle φ1 = 0°
B = 7.5 m × sin(0°) = 0 m
Step (c): Dimension C – Offset Due to Conductor Swing (φ2)
Step C1: Calculate Wind Load per Meter
Wind Load = Wind Pressure × Conductor Diameter
= 927 × 0.02772 = 25.7 N/m
Conductor Weight per Meter = 1.461 × 9.81 = 14.32 N/m
tan(φ2) = 25.7 / 14.32 = 1.794
φ2 = arctan(1.794) ≈ 61°
Step C2: Calculate Horizontal Swing
Swing offset = Sag × sin(φ2)
= 13.0 × sin(61°) ≈ 13.0 × 0.8746 = 11.37 m ≈ 11.40 m
Step C3: Add Offset Due to Bundle Conductor
Assume bundle spacing = 0.90 m
Additional offset = (0.90 / 2) × cos(61°)
= 0.45 × 0.4848 ≈ 0.22 m
Total C = 11.40 + 0.22 = 11.62 m ≈ 11.50 m (rounded)
Step (d): Dimension D – Horizontal Clearance to ROW Edge
D = 2300 mm + 2193 mm = 4493 mm = 4.50 m
Step (e): Dimension E – Distance from Tower Center to ROW Edge (One Side)
E = A + B + C + D
E = 7.60 + 0 + 11.50 + 4.50 = 23.60 m ≈ 24.0 m
Final ROW Width
Total ROW = 2 × E = 2 × 24.0 = 48.0 m
To allow for variation in sag, swing, and construction tolerance, use standard width:
Final ROW = 50.0 m
📌 Summary Table
| Dimension | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| A | Tower center to V-string center | 7.60 m |
| B | Offset due to insulator swing | 0.00 m |
| C | Offset due to wind swing + bundle | 11.50 m |
| D | Clearance to ROW edge | 4.50 m |
| E | Tower center to ROW edge (one side) | 24.0 m |
| ROW | Total ROW width | 50.0 m |
Formula Summary for Right-of-Way Calculation
1. Insulator Swing Offset (Dimension B):
B = L × sin(φ₁)
L = Insulator length (including hardware)
φ₁ = Insulator swing angle (0° for V-string)
2. Conductor Swing Angle due to Wind (φ₂):
φ₂ = arctangent(F_w / W)
F_w = Wind load per meter = Wind pressure × Conductor diameter
W = Conductor weight per meter = Mass × 9.81
3. Horizontal Swing Offset due to Wind (Dimension C):
C₁ = Sag × sin(φ₂)
Additional offset for bundle conductors:
C₂ = (Bundle spacing / 2) × cos(φ₂)
Total conductor swing offset:
C = C₁ + C₂
4. Clearance to Edge of ROW (Dimension D):
D = Basic clearance + Safety margin
5. Total Distance from Tower Center to ROW Edge (Dimension E):
E = A + B + C + D
A = Tower center to insulator string center
6. Total Right-of-Way Width:
ROW Width = 2 × E

Pingback: KML vs KMZ: Why KMZ Files Are Essential for OHTL Plan & Profile Submissions - ohtldesign.com