Introduction
Renewable energy is no longer a choice—it’s the future. From offshore wind farms in the UK to massive solar fields in the US, the clean energy revolution is accelerating. But one question remains: How do we deliver this green power efficiently over long distances?
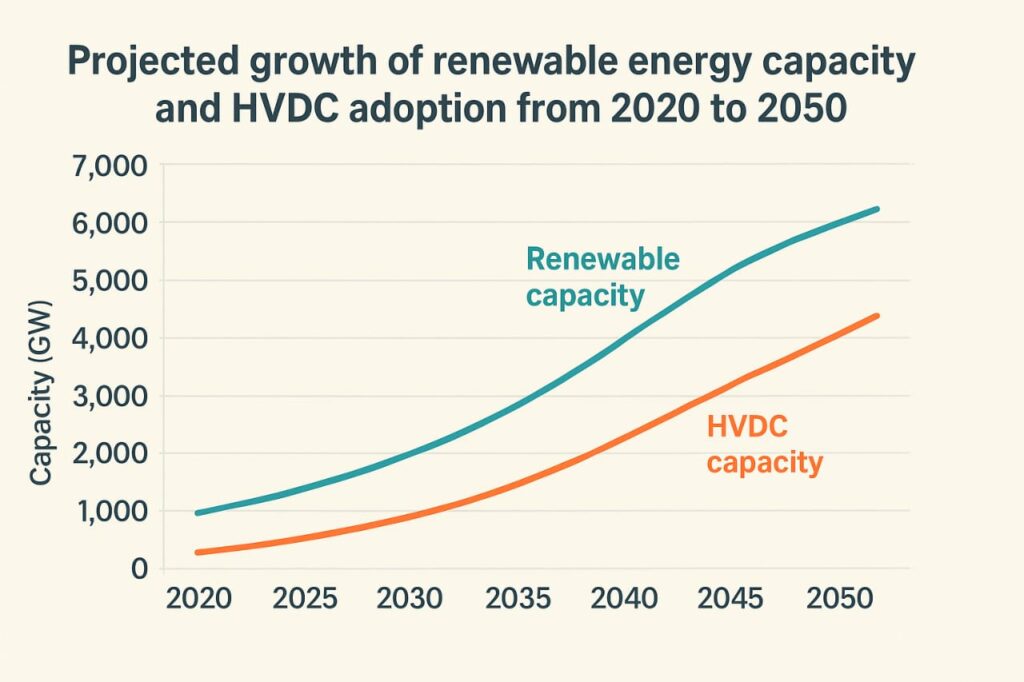
The answer lies in HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) transmission lines. Unlike traditional AC systems, HVDC offers lower losses, better stability, and the ability to move electricity across hundreds of miles with minimal waste. By 2050, HVDC grids could become the backbone of global renewable energy systems.
ALSO READ: Impact of Renewable Energy Integration on Transmission Line Design: Challenges & Solutions
What is HVDC Transmission?
High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) is a power transmission technology that uses direct current instead of alternating current for bulk power transfer.
- HVAC (Alternating Current): Traditional method, efficient only for short distances.
- HVDC (Direct Current): Ideal for long-distance, underground, and offshore renewable integration.
HVAC vs HVDC – Comparison Table
| Feature | HVAC (Traditional) | HVDC (Modern) |
|---|---|---|
| Transmission Losses | High | 30–40% lower |
| Best Distance Use | < 500 km | > 500 km |
| Cost (Initial) | Lower | Higher |
| Maintenance | Higher | Lower |
| Renewable Integration | Moderate | Excellent |
Why HVDC is Key for Renewable Energy
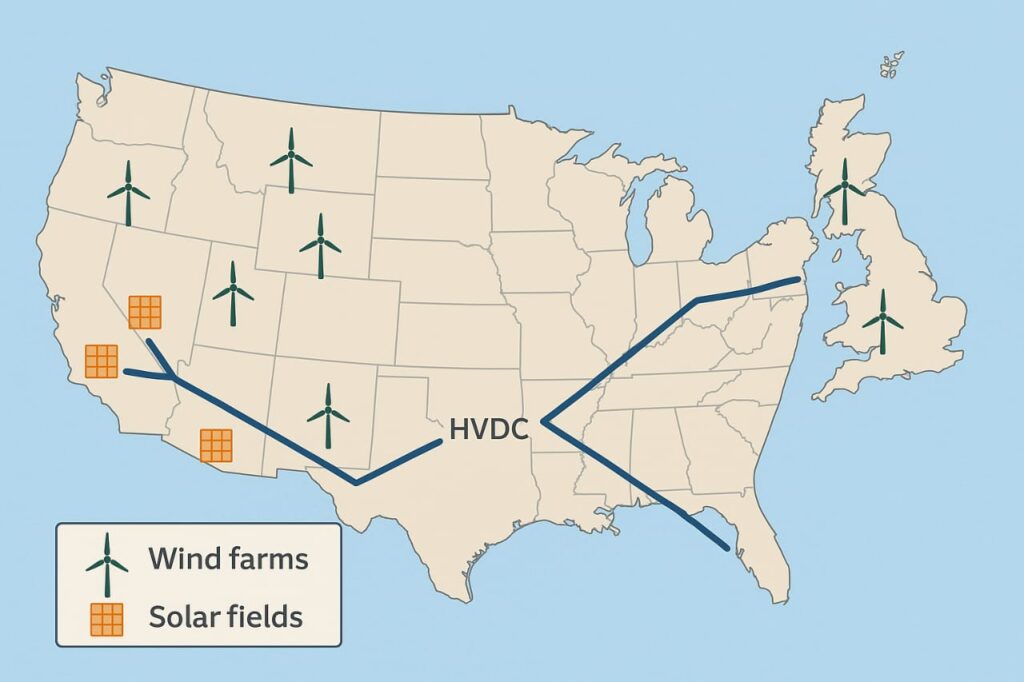
- Offshore Wind Farms (UK): The North Sea wind farms require long-distance transmission. HVDC ensures minimal loss.
- Solar Power in Remote Areas (US): Desert solar fields need HVDC to move electricity to urban demand centers.
- Grid Interconnections: HVDC enables linking countries’ grids, supporting global power trade.
- Stability: HVDC stabilizes fluctuating renewable generation, ensuring consistent supply.
Case Studies: HVDC in Action
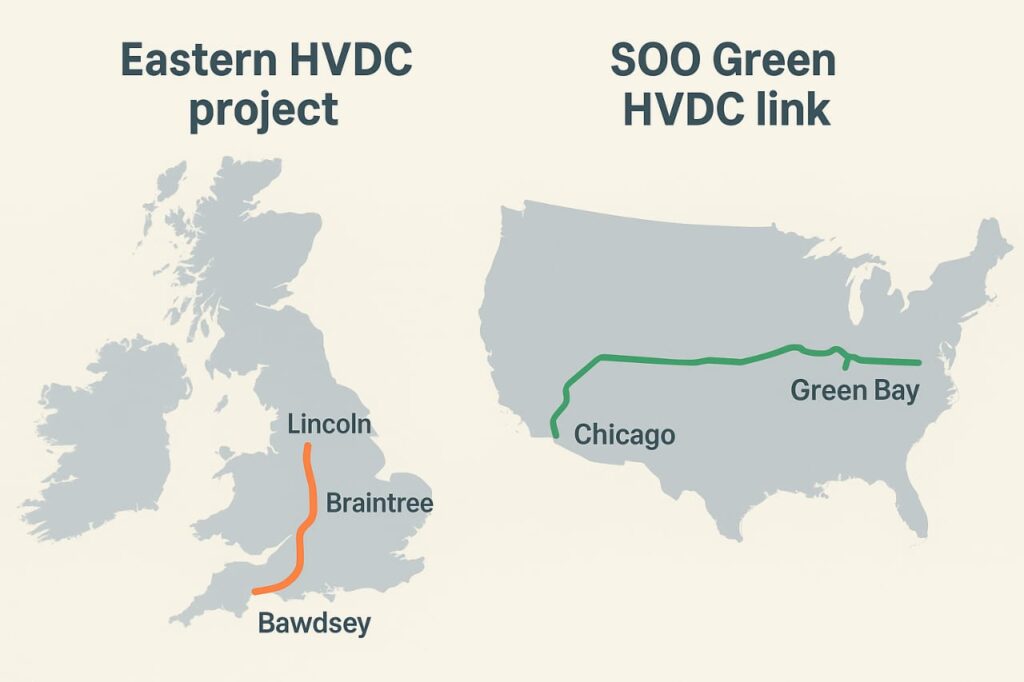
UK – The Eastern HVDC Project
- Connects Scotland to England via subsea cable.
- Capacity: 2 GW, enough for over 2 million homes.
- Supports expansion of North Sea offshore wind power.
US – The SOO Green HVDC Link
- Underground HVDC cable project from Iowa to Illinois.
- Transports renewable energy without affecting landscapes.
- Seen as a model for future US interstate HVDC networks.
Challenges of HVDC Adoption
- High Initial Investment: Converter stations are expensive.
- Complex Engineering: Specialized technology required.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Permitting and cross-border approvals take time.
- Public Acceptance: Concerns about land use for overhead lines.
The Future of HVDC in Renewable Integration
The future energy grid will be smarter, greener, and more connected.
- Smart Grids + AI: Predictive maintenance and intelligent monitoring.
- Cross-Border Power Trading: Europe and North America may develop HVDC highways.
- Net Zero 2050 Goals: HVDC enables large-scale renewable integration to meet emission targets.
Conclusion
The global shift to renewable energy demands a stronger, smarter, and more efficient transmission system. HVDC is not just a technology—it is the backbone of the clean energy transition.
By connecting offshore wind farms, desert solar projects, and even cross-country grids, HVDC ensures the power of tomorrow is delivered without waste.
👉 For engineers, policymakers, and investors, HVDC is the key to building a sustainable, net-zero future.

