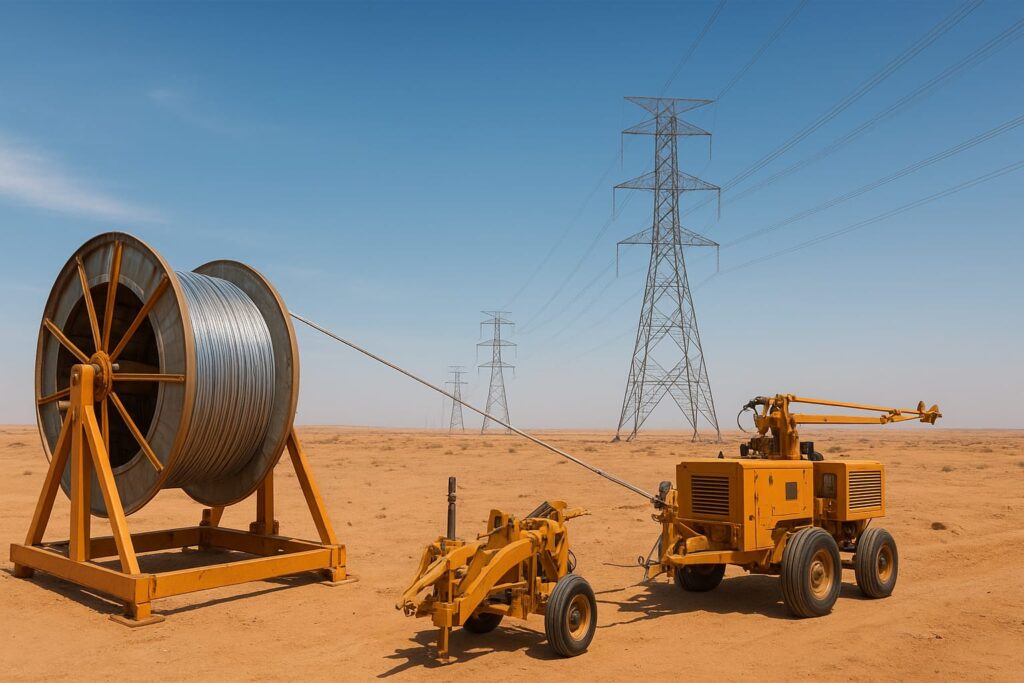
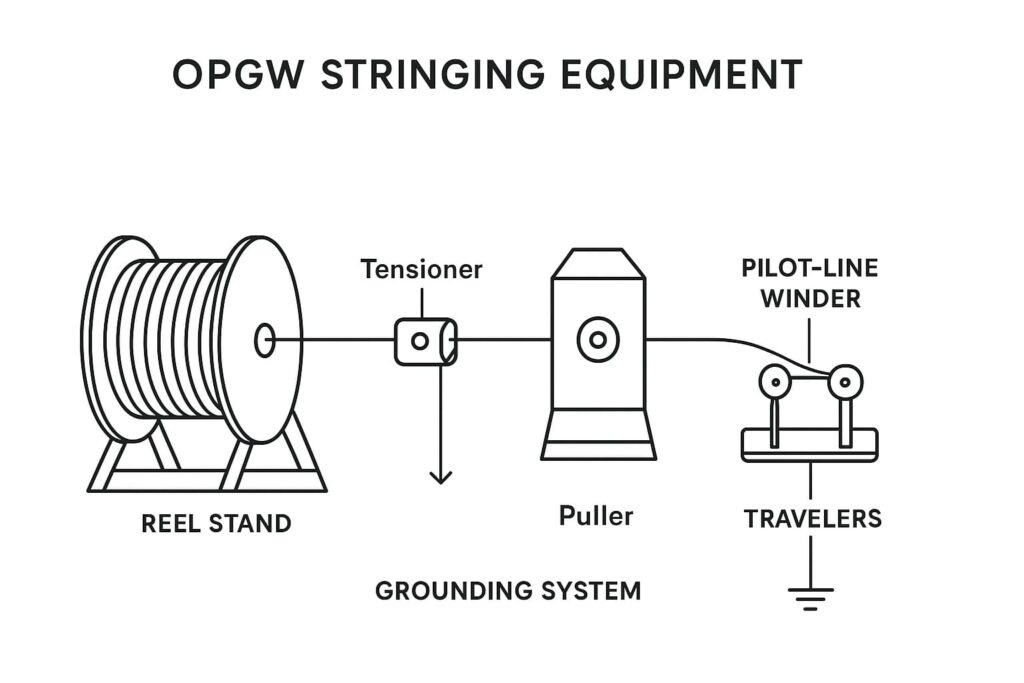
During Optical Fiber Ground Wire (OPGW) installation, choosing the right equipment is just as important as selecting the correct stringing method.
Improper setup can cause fiber breakage, bending stress, or surface damage, all of which compromise both the mechanical strength and optical performance of the cable.
In Saudi Arabia and Middle Eastern power utilities, specific equipment configurations and operating limits are widely followed to ensure safe and controlled OPGW installation.
1️⃣ Reel and Reel Stand Setup
Purpose
The reel and stand hold the OPGW drum securely during payout. They maintain steady back-tension while the cable is fed into the tensioner.
Best Practices
- Always place the reel upright, not on its side.
- Keep protective lagging until the reel is positioned for stringing.
- Align the reel directly with the tensioner to avoid cable scraping.
- Maintain minimum 8 m distance between reel and tensioner.
- Apply a controlled braking system to prevent over-running or backlash.
Reel stands in the Middle East are typically designed to handle large-diameter OPGW drums and include mechanical or hydraulic brakes for consistent control.
ALSO READ: Slack vs Tension Method – Complete Guide to OPGW Stringing
2️⃣ Puller and Tensioner
Role in Installation
The puller applies the pulling force, while the tensioner keeps the cable off the ground under constant load. Together, they form the heart of the tension stringing method.
Operating Characteristics
- Both systems must run smoothly with no sudden jerks or shocks.
- Each must have tension-indicating devices for constant monitoring.
- Bullwheel diameter should be about 70 × the OPGW diameter.
- Grooves should be semicircular and elastomer-lined, not “V”-shaped.
- Maintain a pulling speed of 2 – 5 km/h for stable operation.
- Use dual bullwheels with multiple grooves to reduce strand stress.
- Apply positive fail-safe brakes when pulling stops.
These specifications ensure that the OPGW strands and optical fibers remain undamaged throughout stringing.
3️⃣ Pilot-Line Winder
Purpose
Used to pre-install the pilot line (usually nylon or synthetic rope) before the OPGW is pulled.
Key Features
- Multiple drums for different line positions.
- Capable of high-speed operation with tension control.
- Includes retardation brakes to regulate line payout.
- Prevents excessive slack or entanglement during long spans.
Pilot-line winders are essential for multi-circuit lines or crossings where precise control is required.
4️⃣ Travelers (Sheaves)
Function
Travelers guide the OPGW through the tower during stringing.
They must support the cable gently, without flattening or twisting it.
Design Requirements
- Sheave Diameter: ≥ 40 × the OPGW diameter.
- Groove Shape: Smooth semicircular profile with 15–20° flare angle.
- Lining: Rubber or elastomer to prevent strand abrasion.
- Depth: At least 25 % greater than OPGW diameter.
- Load Display: Each traveler must show safe working load permanently.
Electrical Characteristics
- Travelers are not relied upon for grounding.
- Install separate traveler grounding leads to bypass induced voltages.
- For energized-line proximity, use dedicated grounding bypass clamps.
Proper traveler setup prevents bending strain and maintains accurate sag alignment.
5️⃣ Grounding and Bonding Equipment
Why It’s Critical
During stringing, the OPGW may become electrically charged by nearby energized circuits or lightning activity.
All machines and conductive components must be bonded together and grounded.
Typical Setup
- Running grounds at the front of puller and tensioner.
- Bonding cables connecting tensioner, reel stand, and OPGW.
- Portable earth rods or structure grounds (resistance ≤ 15 Ω).
- Visual check before each shift to ensure ground continuity.
Proper grounding not only protects personnel but also prevents fiber tube damage caused by electrical arcing.
6️⃣ Communication System
Effective, reliable communication between puller, tensioner, and intermediate towers is essential during OPGW stringing.
Field crews across the Middle East typically use:
- Two-way radios or headsets with backup systems.
- Signal codes (hand or flag) when radio fails.
- A dedicated spotter at each critical point for safety confirmation.
7️⃣ Field Arrangement and Alignment
Before stringing starts:
- Select level ground for puller and tensioner placement.
- Ensure clear, straight alignment between equipment and first tower.
- The slope from tensioner to traveler should not exceed 3 : 1 (H : V).
- Verify anchor stability for puller and tensioner units.
- Check that reel direction matches the lay of the OPGW (right-hand lay enters from left, exits right).
These layout details directly influence tension uniformity and fiber safety.
8️⃣ Equipment Checklist Before Operation
| Category | Equipment | Inspection Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Reel Section | Reel stand & brakes | Rotation, stability, reel alignment |
| Tension Unit | Bullwheels & linings | Groove condition, diameter ratio |
| Puller Unit | Drums & controls | Smooth tension control, brake test |
| Travelers | Sheave condition | Lining wear, load marking visible |
| Grounding | Earth rods, cables | Resistance ≤ 15 Ω, tight bonding |
| Communication | Radios, flags | Signal clarity, battery check |
| Safety Gear | PPE, barriers | Ground mats, helmets, gloves |
A quick field inspection of these items reduces downtime and ensures compliance with best practice.
9️⃣ Common Equipment Mistakes to Avoid
- Using undersized bullwheels without rubber lining.
- Placing reel too far from the tensioner, causing sag.
- Operating without proper communication between ends.
- Using travelers with narrow grooves or metallic surfaces.
- Forgetting temporary grounds before stringing.
Following these preventive measures eliminates most fiber-related failures during installation.
🔟 Conclusion
Every successful OPGW installation depends on proper equipment setup and operation discipline.
From reel stand alignment to traveler design, each element plays a key role in protecting the delicate optical fibers inside the ground wire.
Utilities in Saudi Arabia and the Middle East have refined these procedures through years of field experience to ensure long-term reliability, minimal maintenance, and efficient communication performance.
By adhering to these proven equipment practices, engineers can achieve both mechanical safety and optical excellence during OPGW stringing.

