Introduction
Optical Fiber Ground Wire (OPGW) installation is a critical activity in overhead transmission line construction. The choice of method affects mechanical safety, fiber integrity, and overall project efficiency.
In Saudi Arabia and many Middle Eastern utilities, two stringing methods are commonly applied:
- Slack (or Layout) Method
- Tension Method
Let’s explore how each works and where it is best used in field conditions.
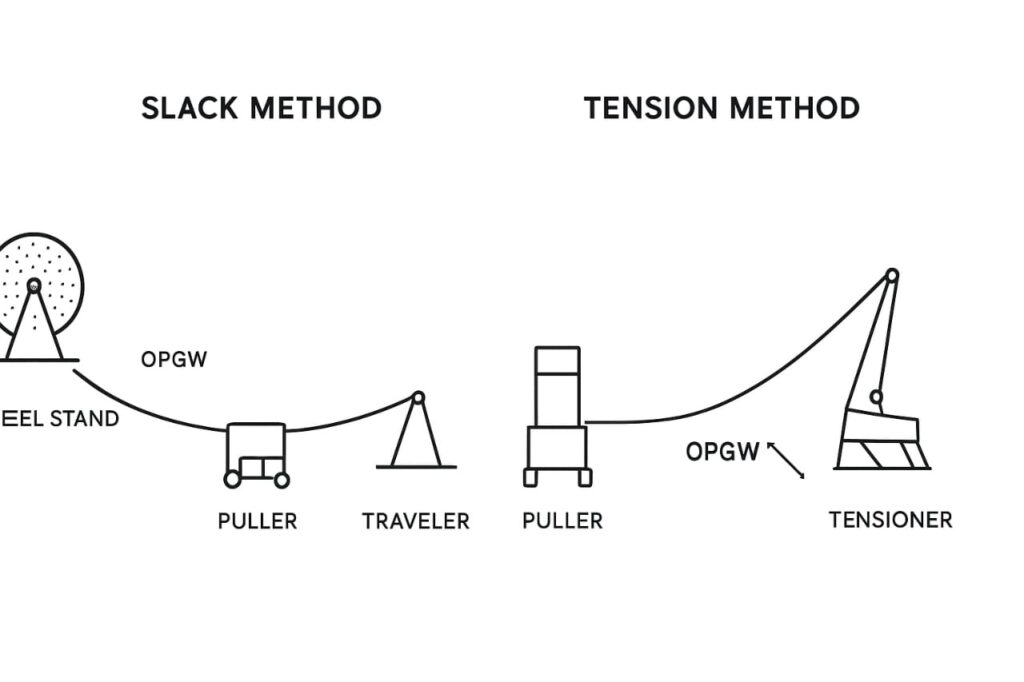
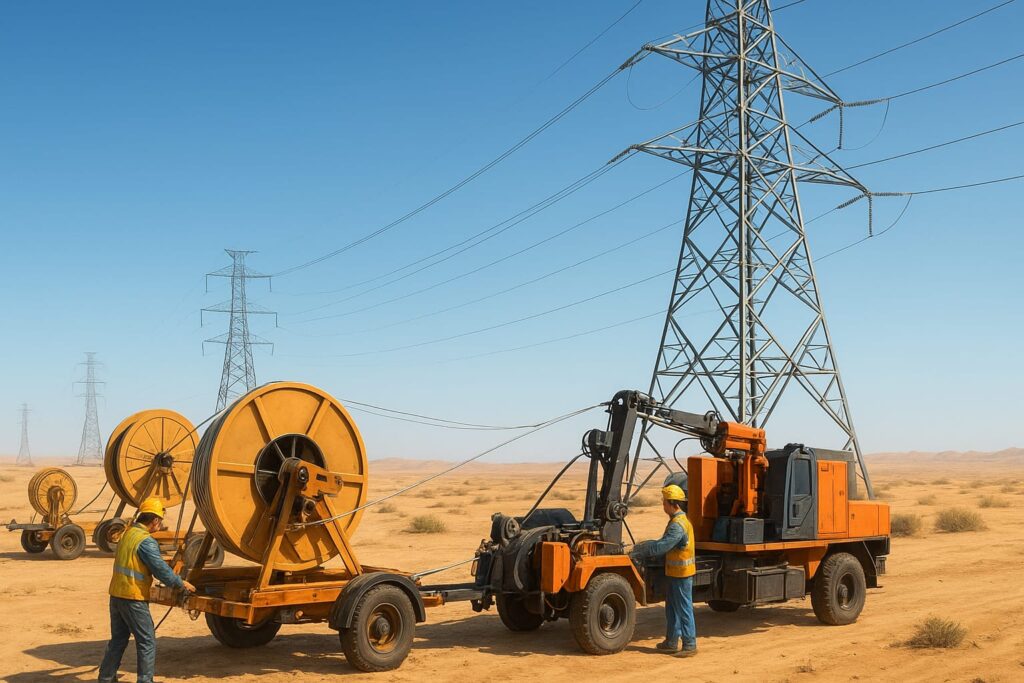
1️⃣ Slack Method (Layout Method)
Principle
The Slack Method involves carrying the OPGW reel along the route and laying the cable on the ground before lifting it into traveler sheaves. It is a basic procedure for short or isolated spans where tension equipment is not available.
Typical Equipment
- Vehicle-mounted reel stands
- Pulling vehicle or tractor
- Braking device to avoid backlash
- Splicing cart or temporary rack
General Procedure
- Mount the reel and move it along the line route.
- Lay the OPGW on the ground while maintaining gentle curvature.
- Stop at each tower, place the wire into the sheaves, and continue to the next span.
- Proceed to sagging and clipping once the section is laid out.
Advantages
- Simple and fast for short spans.
- Low setup cost.
- Useful for repairs or temporary installations.
Limitations
- Cable contacts the ground → risk of fiber damage.
- Not advised for sandy, rocky, or urban areas.
- Limited to short sections only.
Typical Use
Small projects, isolated lines, or emergency works when tension equipment cannot be mobilized.
2️⃣ Tension Stringing Method
Principle
The Tension Method keeps the OPGW under controlled tension throughout stringing, preventing ground contact and fiber abrasion. It is the preferred method across most Middle Eastern utilities for long spans and high-voltage projects.
A light pilot line is first pulled through the traveler sheaves; the OPGW is then pulled using a tensioner and puller set that maintains constant load.
Key Equipment
- Reel stands aligned with tensioner
- Hydraulic tensioner with neoprene-lined bullwheels
- Puller unit with constant tension control
- Pilot-line winder and reel winder
- Grounding system and communication links between teams
Field Setup Tips
- Align reel → tensioner → first tower in a straight line (min. 8 m spacing).
- Maintain smooth pulling speed (≈ 2 to 5 km/h).
- Bullwheel diameter ≈ 70 × OPGW diameter for safe bending.
- Ground equipment at both tension and pull ends.
Advantages
- Prevents surface damage to fibers.
- Maintains proper clearance from energized circuits and terrain.
- Reduces right-of-way travel by heavy machinery.
- Provides uniform tension for accurate sagging.
Limitations
- Requires specialized machines and skilled operators.
- Higher initial equipment cost.
- Demands good communication between puller and tensioner crews.
Typical Use
Standard method for 132 kV and above lines, especially in desert or mountain terrains where ground contact is unsafe.
3️⃣ Safety and Communication
Effective communication between pulling and tension teams is vital. Crews typically use two-way radios or fiber-based headsets.
All metallic equipment must be bonded and grounded to avoid induced voltages from nearby energized lines.
Ground resistance below 15 ohms is recommended for temporary grounds in Middle Eastern utility standards.
4️⃣ Choosing Between Slack and Tension Methods
| Criteria | Slack Method | Tension Method |
|---|---|---|
| Span Length | Short (< 300 m) | Long (> 300 m) |
| Terrain | Flat, rural area | Hilly or urban crossings |
| Equipment | Basic vehicles | Specialized puller/tensioner |
| Cable Protection | Low | High |
| Recommended Use | Temporary or emergency works | Standard OPGW installation |
5️⃣ Field Precautions and Best Practices
- Avoid sharp bends; follow minimum radius of 40 × cable diameter.
- Maintain even tension and avoid jerks during pulling.
- Always install temporary grounds before starting.
- Never reeve OPGW from the wrong direction on bullwheels.
- Test fiber continuity before and after stringing using OTDR.
- Install vibration dampers within 24 hours after clipping.
Following these steps ensures both mechanical and optical integrity throughout the line’s lifecycle.
6️⃣ Conclusion
Both Slack and Tension methods are used in transmission projects across Saudi Arabia and the Middle East, but tension stringing is the industry standard for long spans and EHV lines.
It offers superior fiber protection, better control, and higher operational safety — making it the preferred choice for modern OPGW installation.
Selecting the right method, using proper equipment, and following strict grounding and communication procedures are key to a successful project.

