Introduction
Transmission line towers are the backbone of modern power grids. To ensure these steel structures can withstand extreme wind, weight, and environmental stresses, they must undergo full-scale tower testing. This process is carried out in specialized tower testing stations using test beds, calibrated load cells, and advanced rigging arrangements.
Tower testing is not only a regulatory requirement but also a crucial quality assurance step before large-scale transmission projects are commissioned.
What is Tower Testing?
Tower testing is the simulation of real-world loads on a full-scale prototype of a transmission tower to verify its structural stability, load-bearing capacity, and safety. The testing process is carried out in accordance with international standards such as IEC 60652 and ASCE 10-15.
Objectives of Tower Testing:
- Verify design calculations and drawings.
- Ensure tower stability under wind, weight, and broken wire conditions.
- Check material performance through deflection and tensile tests.
- Confirm compliance with client and international specifications.
Tower Testing Process – Step by Step
1. Assembly & Erection
The tower is first assembled horizontally on the ground as per erection drawings, using cranes and forklifts. It is then erected vertically on a specially fabricated test bed to simulate real foundation conditions.
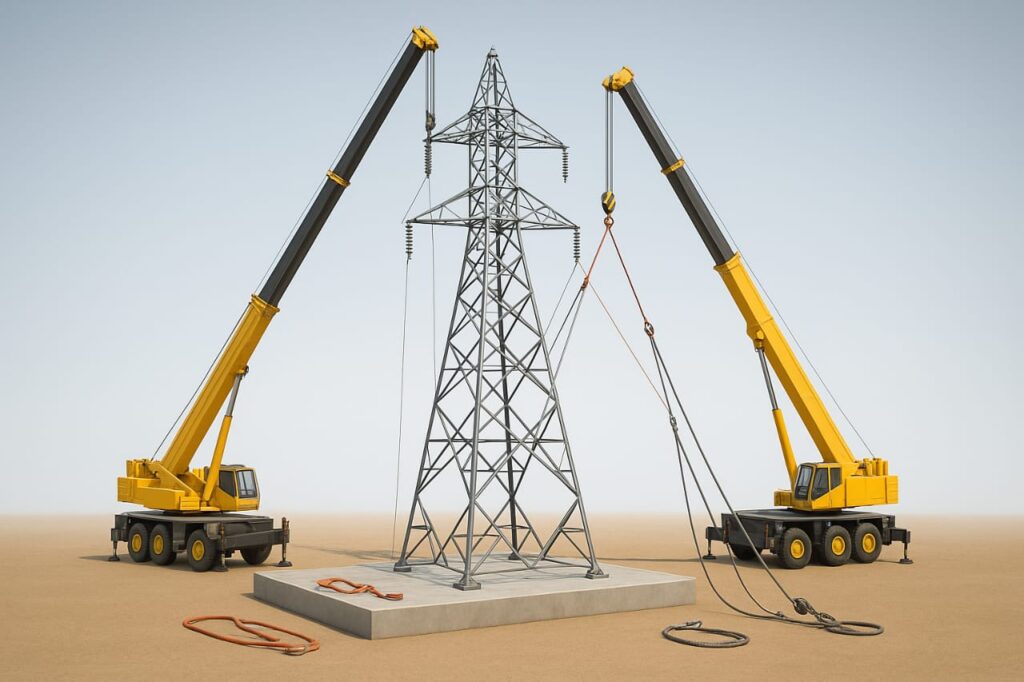

2. Pre-Calibration of Load Cells
Load cells (devices that measure applied forces) are calibrated in accredited laboratories to ensure accuracy.
3. Rigging & Load Application
Wire ropes, winches, and pulleys are used to apply transverse, longitudinal, and vertical loads to the tower. These loads simulate wind forces, conductor weight, and extreme environmental conditions.
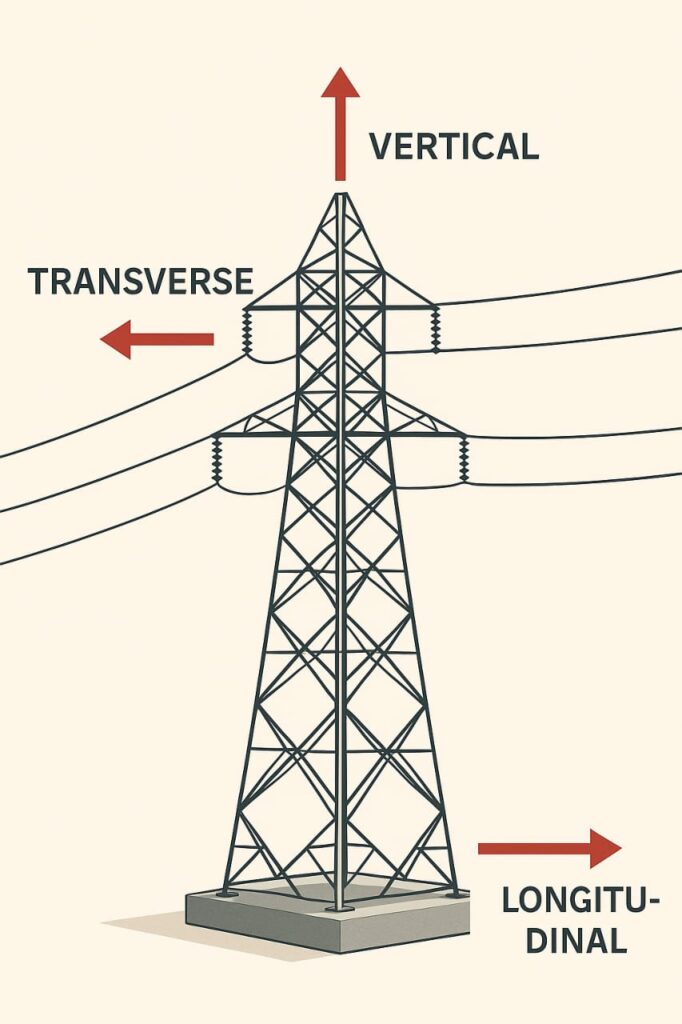
4. Load Test Sequence
Typical test conditions include:
- Standard Wind Condition – testing tower stability under maximum wind loads.
- Heavy Vertical Load – simulating maximum conductor weight.
- Broken Wire Condition – ensuring stability when one or more conductors fail.
- Destruction Test – loading beyond 100% to find ultimate failure point.
5. Deflection & Observation
Deflections are measured using theodolites and scales at multiple points on the tower to check bending and sway.
6. Post-Calibration & Reporting
After testing, load cells are recalibrated, and a detailed test report is issued within 30 days, certifying compliance.
Importance of a Tower Testing Bed
The test bed is a massive foundation-like structure where the tower is erected. It ensures:
- Accurate load transfer during testing.
- Stability and safety of testing operations.
- Realistic simulation of in-field tower behavior.
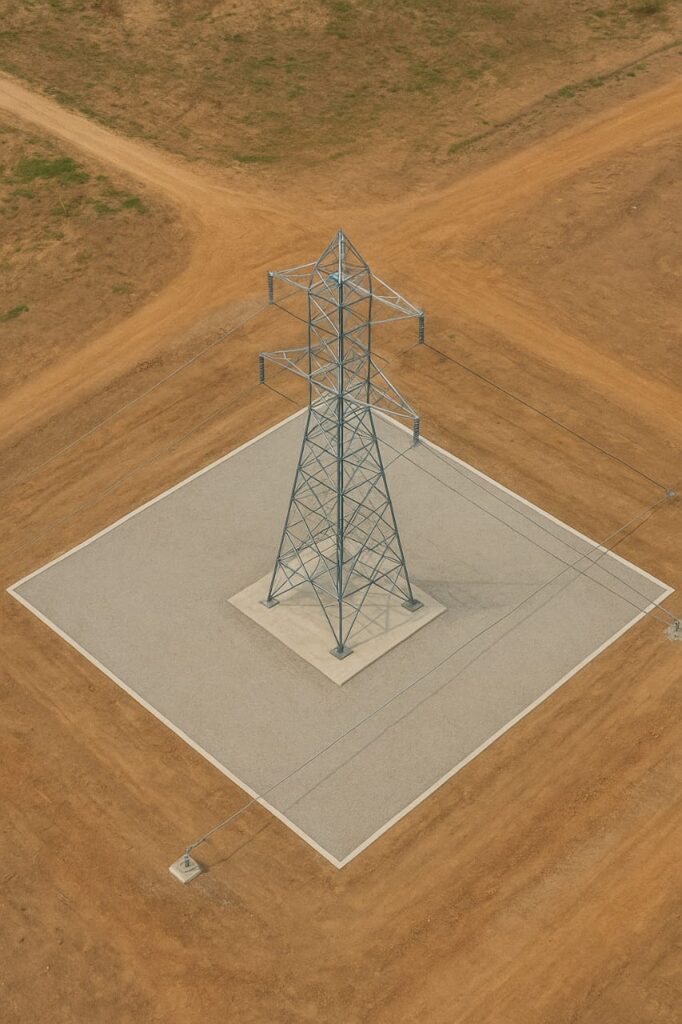

Tower Testing Standards
Most tower testing worldwide follows these standards:
- IEC 60652 – International Electrotechnical Commission standard for tower load testing.
- ASCE 10-15 – American Society of Civil Engineers’ guidelines for steel transmission structures.
- Client-specific specifications – e.g., utilities like Power Grid Corporation of India (PGCIL) or Saudi Electricity Company (SEC).
Tower Testing Facilities in India
India is a global hub for transmission tower manufacturing and testing, with several world-class facilities, including:
- Central Power Research Institute (CPRI) – Bengaluru.
- PGCIL Tower Testing & Research Station – Hyderabad.
- KEC International Test Station – Jaipur.
- Larsen & Toubro (L&T) Tower Testing Facility – Kanchipuram.
- Kalpataru Power Transmission Ltd. (KPTL) – Gandhinagar.
- Sterlite Power Tower Testing – Haridwar.
- SKIPPER Limited
- Jyoti Structure Limited
Tower Testing in the Middle East
The Middle East also has specialized testing stations supporting mega-scale transmission projects:
- Al-Babtain Power & Telecom Tower Testing Station – Saudi Arabia.
- Elsewedy Electric Testing Facility – Egypt (serving the region).
- SEC & Local EPC Contractors’ Test Facilities – Saudi Arabia and UAE.
Why Tower Testing Matters for Transmission Projects
Tower testing ensures:
- Safety – preventing collapse in extreme weather.
- Reliability – uninterrupted power supply.
- Cost Savings – avoiding design errors and failures during construction.
- Compliance – meeting international and regional power utility standards.
Conclusion
As the demand for reliable power grows across India, the Middle East, and beyond, tower testing has become an indispensable step in transmission line projects. With state-of-the-art facilities, rigorous testing protocols, and adherence to global standards, the process guarantees that every tower erected is safe, durable, and performance-proven.



That is really interesting. I’ve worked on towers for the last 20 years as an Engineer/PM, but never realised the testing behind the tower construction
That’s wonderful to hear! With your 20 years of hands-on experience in towers, your perspective is invaluable. The testing and design verification side often stays behind the scenes, but it plays a huge role in ensuring reliability and safety. Glad the post could bring a new angle to your already rich experience in this field!
Nice..but Jsl and skipper is missing…
Thank you, I have updated the article.
Earthwire /opgw cable
Testing details
Pingback: How to Assemble OPGW Accessories on Terminal Towers - ohtldesign.com
Pingback: Anti-Climbing Barriers for Transmission Towers: Importance, Standards, and Design - ohtldesign.com
Pingback: Role of Synchronous Condensers in Modern Power Systems (2025) - The World of Engineers
Pingback: The Future of Electrical Engineering: Trends Shaping the Next Decade - The World of Engineers
Pingback: Feeder Protection Signaling - The World of Engineers
Pingback: How do you select cable size for a motor or load - The World of Engineers
Pingback: Synchronous Condenser, STATCOM, STATCOM with BESS, and SVC - The World of Engineers
Pingback: Electrical Safety MCQs: Practice Quiz for Engineers - The World of Engineers
Pingback: Classification of Lightning Protection Systems - The World of Engineers
Immerse yourself in an exciting world show drone, where technology and art merge in an incredible spectacle.
As costs decrease, drone shows may become accessible to a broader range of events worldwide.